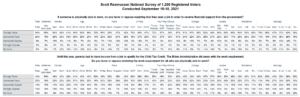
If someone is physically able to work, 78% of voters believe they should be required to seek a job in order to receive financial support from the government. A Scott Rasmussen national survey found that 13% disagree and 9% are not sure.
A solid majority of every measured demographic group supports the work requirement. That includes 86% of Republicans, 76% of Independents, and 73% of Democrats.
Overall, 54% Strongly Favor work requirements and 4% are Strongly Opposed.
Earlier this year, the Biden Administration removed work requirements for the Child Care Tax Credit. Sixty-six percent (66%) of voters favor restoring the work requirement for all who are physically able to work. Twenty-four percent (24%) are opposed.
Restoring the work requirement is favored by a majority of every measured demographic group. That includes 75% of Republicans, 65% of Democrats, and 57% of Independents.
SIGN UP to receive Scott’s free email newsletter.
CHECK OUT Scott’s latest polls.
Note: Neither Scott Rasmussen, ScottRasmussen.com, nor RMG Research, Inc. have any affiliation with Rasmussen Reports. While Scott Rasmussen founded that firm, he left more than seven years ago and has had no involvement since that time.
* If someone is physically able to work, do you favor or oppose requiring that they seek a job in order to receive financial support from the government?
54% Strongly favor
24% Somewhat favor
9% Somewhat oppose
4% Strongly oppose
9% Not sure
* Until this year, parents had to have income from a job to qualify for the Child Tax Credit. The Biden administration did away with the work requirement. Do you favor or oppose restoring the work requirement for all who are physically able to work?
44% Strongly favor
22% Somewhat favor
14% Somewhat oppose
10% Strongly oppose
10% Not sure
Methodology
The survey of 1,200 Registered Voters was conducted by Scott Rasmussen using a mixed mode approach from September 16-18, 2021. Field work for the survey was conducted by RMG Research, Inc. Most respondents were contacted online or via text while 263 were contacted using automated phone polling techniques. Online respondents were selected from a list of Registered Voters and through a process of Random Digital Engagement. Certain quotas were applied, and the sample was lightly weighted by geography, gender, age, race, education, internet usage, and political party to reasonably reflect the nation’s population of Registered Voters. Other variables were reviewed to ensure that the final sample is representative of that population.
The margin of sampling error for the full sample is +/- 2.8 percentage points.